
Purpose: to reprogram / recode the new battery of all its data after replacement.
Warning! There are 5 lines of coding to do here.
Proceed :
1 – Engine off, ignition off, connect your official VAG-COM VCDS cable to the computer, then plug the other end into your vehicle’s diagnostics socket.
2 – Switch on the ignition and run the VCDS program.
Line 1:
3 – Click on“Select”, then click on“19 – CAN Gateway”.
4 – Click on “Adaptation – 10”.
5 – On this page, at the very top, there is a drop-down menu.
In this drop-down menu, choose“Adaptation batterie-Capacité nominal de la batterie”.
6 – On this same page, there is a second drop-down menu, but towards the bottom
of the page.
On this menu, choose a nominal value indicated on your battery, e.g.“70Ah”.
Line 2:
3 – Click on“Select”, then click on“19 – CAN Gateway”.
4 – Click on“Adaptation – 10”.
5 – On this page, at the very top, there is a drop-down menu.
In this drop-down menu, choose“Adaptation batterie-Technologie de la batterie”.
6 – On this same page, there is a second drop-down menu at the bottom
of the page.
On this menu, choose a corresponding value
Ex: In the case of VARTA E39 choose“Etoffe”.
Line 3:
3 – Click on“Select”, then click on“19 – CAN Gateway”.
4 – Click on“Adaptation – 10”.
5 – On this page, at the very top, there is a drop-down menu.
In this drop-down menu, choose“Adaptation batterie-Fabriquant de batterie”.
6 – On this same page, there is a second drop-down menu at the bottom
of the page.
On this menu, choose the corresponding brand:
Ex: In the case of the VARTA E39, choose“VAO”.
Line 4:
3 – Click on“Select”, then click on“19 – CAN Gateway”.
4 – Click on“Adaptation – 10”.
5 – On this page, at the very top, there is a drop-down menu.
In this drop-down menu, choose“Adaptation batterie-Numéro de série de la batterie”.
6 – On this same page, there is a second drop-down menu, but at the bottom
of the page.
On this menu, enter the corresponding serial number:
Warning, insert only the last 10 digits of the serial number.
Line 5 (option for AGM battery):
3 – Click on“Select”, then click on“19 – CAN Gateway”.
4 – Click on“Coding – 07” then click on“Long Coding Wizard”.
5 – Select byte“3” then byte“3”.
6 – Then change bit 4-7 to“30-Battery Architecture/Type: Absorbent Glass Matt (AGM)” and confirm.
Battery status detection functions :
Battery status detection in the battery data module calculates the following quantities, which are transmitted via the LIN bus to the J533 data bus diagnostics interface:
1 “Battery non-existent” detection: if the battery data module detects no battery for
more than 30s, a corresponding bit is set to a
2 voltage momentarily allowing optimum charging of the battery
3 “Motor startability” bit. This indicates whether the battery is momentarily able to start
the engine or not
4 charge that can momentarily still be drawn from the battery before reaching the limit of
ability to start the engine
5 current state of charge of the battery
6 battery ageing. Battery ageing can be determined via quantities such as
energy storage capacity and momentary battery power.
7 battery quiescent voltage
8 battery internal resistance
The battery sensor in the battery monitoring ECU J367:
Knowing whether the battery has sufficient electrical energy to restart the engine is essential information for start-stop operation.
The ECU is located directly on the “negative” terminal of the ground cable and is connected to the diagnostic interface via the LIN data bus.
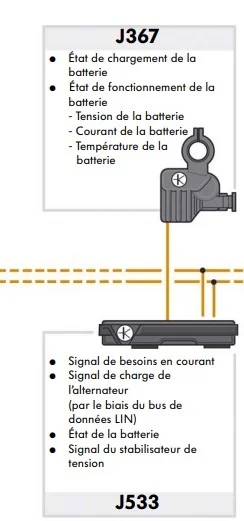
Signal usage:
The battery sensor records the following values:
– Battery temperature
– Battery voltage
– Charging current
The battery temperature is obtained from a map and the ambient temperature.
It also enables deductions to be made about the battery’s charging time.
Using the data obtained in this way, it is possible to adapt the charging control, in particular the charging voltage, to the battery’s charging and operating status. The aim is to increase the availability of the start-stop device by optimizing the use of starter battery data.
Consequence in the event of a fault
If the battery sensor is faulty, the battery condition can no longer be correctly detected.
A fault is stored in the fault memory of the data bus diagnostic interface. The start-stop device is disconnected.
Battery
The vehicle’s battery is housed in the engine compartment and protected by a battery tray. Battery size and design depend on engine version, equipment and national variant. Standard, EFB and AGM batteries are used.
Vehicles with petrol engines and start/stop systems are fitted with EFB batteries, while vehicles with diesel engines and start/stop systems are fitted with AGM batteries. Vehicles with stationary chauffage generally have an AGM battery.
EFB
An EFB (Enhanced Flooded Battery) is a reinforced wet battery. The positive plate inside the battery is coated with an additional polyester canvas. This gives the battery’s active mass additional support on the plate. The alternating cycle resistance of these batteries is superior to that of standard batteries. During charging, the EFB battery is treated like a standard battery.
AGM battery
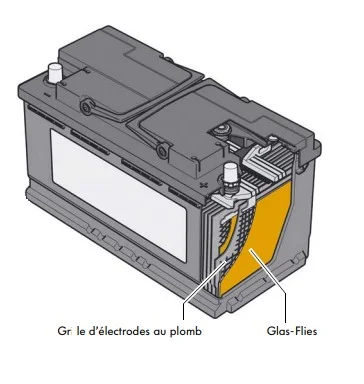
In AGM batteries (short for Absorbent Glass Mat), the battery’s electrolyte is retained in a micro-porous glass mat. An AGM battery is not only even more resistant to alternating cycles than an EFB battery, but also watertight. When charging, follow the charger’s operating instructions and select the AGM battery program if necessary.
In the case of AGM batteries, the automotive battery electrolyte is retained in a micro-porous glass mat. In addition to
increased resistance to alternating cycles, an AGM battery is characterized by its good sealing properties. Waterproofing is of crucial importance
, especially when the battery is installed in
the passenger compartment. When charging, please follow the charger’s operating instructions and select the program for
AGM battery, if applicable.
Below we see the battery brand, serial number and manufacturer.

